PROLAPSED INTERVERTEBRAL DISK
Prolapsed intervertebral disk is also known as Slipped disk or Herniated disk. It is a spinal condition where the gel like nucleus of the spinal disk pushing out through the disk’s outer layer. This can occur anywhere along the spine.
Commonest site:
Between L4-L5 (Lumber spine)
Between C5-C6 (Cervical spine)
Un commonest site:
Above L3-L4 level
Some people who experience pain related to a herniated disk often remember a causing event that caused their pain. Unlike back pain, herniated disk pain is often burning or stinging, and may radiate into the lower extremity. In severe cases there can be associated with weakness or sensation changes. In some of the cases a herniated disk injury may compress the nerve or the spinal cord which causes consistent pain leading to nerve compression or spinal cord dysfunction.
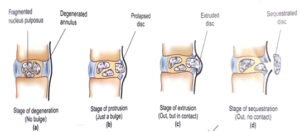
STAGESOF HERNIATION
- Nucleus degeneration : During this stage, the outer wall of a disk weakened, but there is no visibility of external changes occurred. It is likely for nerve compression to occur at this stage.
- 2. Disk prolapse : The outer wall of the disc begins to change shape and bulge out into the spinal canal. There may begin to feel symptoms at this stage if the damaged disk exerts pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots that extend from it.
- 3. Extrusion : In this stage , the gel-like(nucleus pulposus) inner core of the disc has broken through a tear in the disk’s outer wall, but the material remains attached to the disk.
- Sequestration : In this final stage, the gel-like substance has left the disk and leaked into spinal canal. In this stage patients are more likely to feel pain.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Severe low back pain which can be radiating pain also.
- Walking can be painful and difficult.
- Muscle spasm, tingling sensation, weakness or atrophy.
- loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Some people may be asymptomatic.
- Slow and deliberate, tip-toe walking.
- Spine, trunk deviation.
EXAMINATION
- Examination of
- Movements
- Present of Tenderness.
- Neurological examination.
Straight leg raise (SLR) test. This test is a very accurate predictor of a disk herniation in patients under the age of 35. During the test, patient lie on back and doctor carefully lifts the affected leg. The knee stays straight. If there is a feeling of pain down the leg and below the knee. It is a strong indication that the person is having a herniated disk.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis is mainly clinical.
Investigations like :
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- X- Ray
- Electromyography (EMG)
TREATMENT
MEDICAL TREATMENT
- such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve).
- Cortisone injections.If the pain doesn’t improve with oral medications, then doctor might recommend a corticosteroid that can be injected into the area around the spinal nerves. Spinal imaging can help guide the needle.
- Muscle relaxers
PHYSICAL THERAPY
Physiotherapy play the vast and most important role in prolapsed intervertebral disk which gives long time relief in pain.
- Muscle Strengthening: Strong muscles are a great support system for spine and better handle pain. If core stability is totally regained and fully under control, strength and power can be trained. Muscle strengthening leads to long time pain management.
- Spinal Manipulative Therapyand Mobilization : Spinal manipulative therapy and mobilization leads to short-term pain relief when suffering from acute low back pain. When looking at chronic low back pain, manipulation has an effect similar to NSAID.
- .Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation(TENS) / IFT : Modalities contribute to pain relief and improvement of function.
- Manipulative Treatment: Manipulative treatment on lumbar disk herniation appears to be safe, effective, and it seems to be better than other therapies. However high-quality evidence is needed to be further investigated.
- Traction: A recent study has shown that traction therapy has positive effects on pain, disability and SLR on patients with intervertebral disk herniation.
- Cryotherapy: It reduces spasm and inflammation in acute phase.
- Shortwave diathermy: Pulsed SWD mostly used in acute condition and continuous SWD in chronic condition.
- Ultrasound: As phonophoresis, it increases extensibility of connective tissues.
- Mild stretching exercises.
- Posture management is one of the most important thing which help in reducing further chances injury


